SEO is vast. It has many parts. Each part serves a purpose. Some focus on websites. Others focus on content. SEO is always changing. Search engines update their rules. Specialists need to adapt.
Describing SEO can be tricky. It has many technical terms. But it can be simple. This guide breaks it down. Each section explains a specialty.
1. Technical SEO
Technical SEO deals with website structure. It ensures search engines can read a site. It focuses on speed, indexing, and security.
1.1 Website Speed
Speed is key. Slow websites lose visitors. Google ranks fast sites higher. Optimizing images and code helps. Using a fast server also matters.
1.2 Mobile-Friendliness
Most people browse on phones. A site must work well on all screens. Google checks for mobile-friendliness. A responsive design is important.
1.3 Secure Websites (HTTPS)
Security builds trust. Google favors secure sites. HTTPS protects users’ data. An SSL certificate is needed.
1.4 Crawlability and Indexing
Search engines scan sites. This is called crawling. Pages must be easy to find. Sitemaps help search engines. Robots.txt files guide them.
1.5 Fixing Errors
Errors hurt SEO. Broken links confuse users. Slow-loading pages frustrate visitors. Fixing these issues improves rankings.
2. On-Page SEO
On-page SEO is about content. It helps search engines understand pages. It also improves user experience.
2.1 Keywords
Keywords tell Google what a page is about. They should be natural. Overusing them can hurt rankings. Researching the right keywords is important.
2.2 Title Tags and Meta Descriptions
Titles should be clear. They should include keywords. Meta descriptions give a summary. They encourage clicks.
2.3 Headings and Structure
Headings organize content. H1 is the main title. H2 and H3 break up sections. They improve readability.
2.4 Internal Linking
Links connect pages. They help users navigate. They also help search engines understand content. Good linking improves rankings.
2.5 Image Optimization
Images should load fast. Alt text helps search engines. It also helps visually impaired users.
3. Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO happens outside the website. It builds authority and trust. It helps a site rank higher.
3.1 Backlinks
Backlinks are links from other sites. They act as votes of confidence. Quality backlinks improve rankings. Spammy links can hurt SEO.
3.2 Social Signals
Social media impacts SEO. Shares, likes, and comments show popularity. They help drive traffic.
3.3 Brand Mentions
When people talk about a brand, Google notices. Even without links, mentions help SEO. Positive mentions build trust.
3.4 Guest Blogging
Writing for other websites helps. It spreads awareness. It earns backlinks. It builds credibility.
3.5 Influencer Outreach
Partnering with influencers boosts visibility. Their audience can bring traffic. This helps SEO indirectly.
4. Local SEO
Local SEO helps businesses appear in nearby searches.
4.1 Google My Business
A business must claim its GMB profile. It should be complete and accurate. Reviews and updates improve rankings.
4.2 Local Keywords
People search for local services. Keywords should include city names. “Best bakery in New York” is an example.
4.3 Citations and Directories
Business listings help SEO. Yelp, TripAdvisor, and other directories matter. The information must be consistent.
4.4 Reviews and Ratings
Good reviews boost rankings. They also build trust. Responding to reviews is important.
4.5 Location Pages
Businesses with multiple locations need pages for each one. Each page should have unique content. It should include address and contact details.
5. Content SEO
Content is the heart of SEO. High-quality content attracts users. It keeps them engaged.
5.1 Blog Writing
Blogs drive traffic. They help with keywords. They build authority.
5.2 Evergreen Content
Some content stays relevant forever. Examples are guides and how-to articles. These bring long-term traffic.
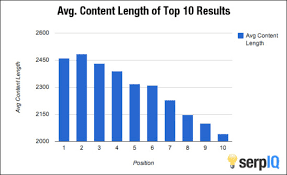
5.3 Content-Length
Longer content often ranks better. But it must be useful. Quality matters more than length.
5.4 User Intent
Content should match what users need. Some users want answers. Others want to buy. Understanding intent helps create better content.
5.5 Updating Conttent
Old content can lose rankings. Updating it helps. Adding new information keeps it fresh.
6. E-Commerce SEO
E-commerce SEO helps online stores rank higher. It improves sales and traffic.
6.1 Product Page Optimization
Each product page should have a clear title. It should include keywords. Descriptions must be detailed and engaging.
6.2 Category Pages
Category pages should be well-structured. They must have unique content. This helps search engines understand them.
6.3 Image SEO
Product images must be optimized. They should load quickly. Alt text helps with search visibility.
6.4 Customer Reviews
Reviews build trust. They also help rankings. Encouraging reviews improves SEO.
6.5 Structured Data
Structured data helps search engines. It creates rich results. This includes prices, ratings, and stock availability.
7. International SEO
International SEO helps websites rank globally. It ensures content reaches the right audience.
7.1 Hreflang Tags
Hreflang tags tell Google which language to show. They prevent duplicate content issues.
7.2 Localized Keywords
Each country has different search terms. Researching local keywords is essential.
7.3 Country-Specific Domains Some businesses use country-specific domains. This helps with local rankings.
7.4 Cultural Adaptation
Translations alone are not enough. Content should match local culture. This improves engagement.
7.5 International Hosting
A local server can improve speed. Faster sites rank better.
8. Voice Search SEO
Voice search is growing. People ask questions differently. SEO must adapt.
8.1 Conversational Keywords
Voice search uses natural language. Phrases should be more conversational. “Where can I buy running shoes?” is an example.
8.2 Featured Snippets
Google often reads snippets aloud. Optimizing for them improves visibility.
8.3 Question-Based Content
Voice searches often start with how,what or why. Creating Q&A-style content helps.
8.4 Mobile Optimization
Most voice searches happen on phones. A mobile-friendly site is crucial.
8.5 Local SEO for Voice
People use voice search for local needs. “Best pizza near me” is a common query. Businesses must optimize for location-based searches.
9. Video SEO
Videos are powerful. They boost engagement. Google ranks videos in search results.
9.1 Video Titles and Descriptions
Titles must be clear. They should include keywords. Descriptions should be detailed.
9.2 YouTube SEO
YouTube is a search engine. Tags, thumbnails, and transcripts help with ranking.
9.3 Transcripts and Captions
Text helps search engines understand videos. Adding captions improves accessibility.
9.4 Video Sitemaps
A video sitemap tells Google about site videos. It helps with indexing.
9.5 Embedding and Sharing
Videos should be easy to share. Embedding them in blogs increases visibility.
10. Mobile SEO
More people browse on phones. Mobile SEO makes sure sites work well.
10.1 Responsive Design
A site must fit all screen sizes. Responsive design adjusts content automatically.
10.2 Mobile Page Speed
Slow pages lose visitors. Compressing images and reducing code speeds up a site.
10.3 Touch Friendly Elements
Buttons should be easy to tap. Text should be readable without zooming.
10.4 Mobile First Indexing
Google looks at the mobile version first. A poor mobile site affects rankings.
10.5 Accelerated Mobile Pages
AMP makes pages load faster. It improves mobile experience.
11. UX and SEO
User experience (UX) affects SEO. A good experience keeps visitors engaged.
11.1 Easy Navigation
Users should find what they need quickly. A simple menu helps.
11.2 Readability
Content should be easy to read. Short sentences and clear fonts help.
11.3 Call to Action
A clear CTA guides users. It tells them what to do next.
11.4 Reducing Bounce Rate
A high bounce rate means users leave quickly. Relevant content keeps them longer.
11.5 Site Accessibility
Sites should work for everyone. Including those with disabilities.
12. Analytics and SEO
Tracking performance is key. Data helps improve SEO.
12.1 Google Analytics
This tool tracks visitors. It shows where they come from.
12.2 Google Search Console
It helps monitor site health. It reports errors and keyword rankings.
12.3 Heatmaps
Heatmaps show where users click. They reveal what grabs attention.
12.4 Conversion Tracking
SEO is not just about traffic. Tracking sales and sign-ups matters.
12.5 A/B Testing
Testing different versions of a page improves performance. Small changes can make a big impact.
13. SEO Trends and Future
SEO is always evolving. Keeping up is important.
13.1 AI in SEO
Search engines use AI. Understanding user intent is key.
13.2 Zero Click Searches
Some searches show answers at the top. Users don’t need to click.
13.3 Experience, Expertise, Authoritatveness, and Trustworthiness
Google values quality content. Experts rank higher.
13.4 Visual Search
People search using images. Optimizing for visual search is growing.
13.5 Sustainability in SEO
Eco-friendly websites are becoming popular. Fast and green hosting helps rankings.
Conclusion
SEO has many specialties. Each one plays a role. Understanding them helps create better strategies. SEO will keep changing. Staying updated is key to success.